In This Section
2016 and 2018 Barriers to Weight Loss and Exercise
Barriers to Weight Loss and Exercise - Weight loss identified as evidence based management strategy for IIH (Mollan et al 2018). Greater weight loss is seen with programmes including strategies to increase physical activity than those targeting diet alone (Wu et al 2009). Increasing physical activity is increasingly incorporated into trials to lower weight in conditions such as migraine (Bond et al 2013). Subjectively people with IIH report losing weight and exercising is challenging and these surveys aimed to identify and rank any perceived barriers.
Survey 1 - In 2016 questionnaire on exercise and weight loss and perceived barriers.
Method - Internet survey via survey monkey
Results - 218 people with IIH responded to the survey. The respondents were predominantly female (213 Female, 5 Male) with a mean age of 32.7 years (standard deviation ± 9 years 7 months). The average length of diagnosis was 5years 3 months (standard deviation ± 6 y 3 m).
Barriers to Weight loss
Participants also described these barriers in their own words:
"I can’t exercise"
"My medication makes it harder to lose weight"
"I find being fatigued makes it exhausting to prepare meals"
Barriers to exercise
Participants further described these barriers to exercise
"...too much cardiovascular sets off my headache…"
"...as soon as my blood pressure/pulse elevates it causes severe pounding in my head..."
"fear and anxiety of the unknown"
"I need to sleep after.."
Participants were also asked if any exercise helped their IIH
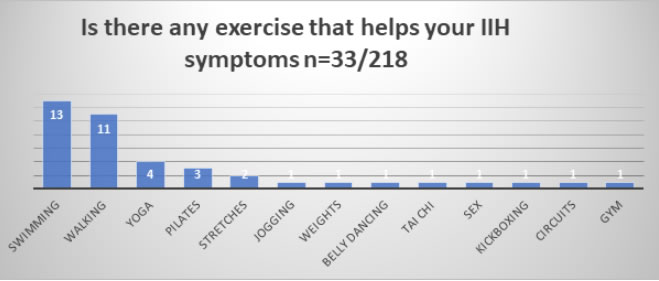
Conclusion
People with IIH experience significant barriers to losing weight and to exercising. These barriers should be explored at greater depth to ensure that people with IIH can receive appropriate support and management.
Survey 2 - 2017 Relative importance of perceived barriers
Background
Survey 1 identified people with IIH perceived barriers to both weight loss and exercise. The second survey asked participants to rank these barriers in order of importance to them.
Method - Internet survey via survey monkey
Results - 164 people with IIH responded to the survey. The respondents were predominantly female (159 Female, 5 Male) with a mean age of 37.8 years (standard deviation ± 9 years 4 months). The average length of diagnosis was 4 years 4 months (standard deviation ± 5 years 6 months). Participants were also asked their weight on diagnosis and current weight and with their height BMI were calculated. Current BMI was 37. 8 (standard deviation ± 8.4) and on diagnosis 39.4 (standard deviation (39.4 ± 8.7)
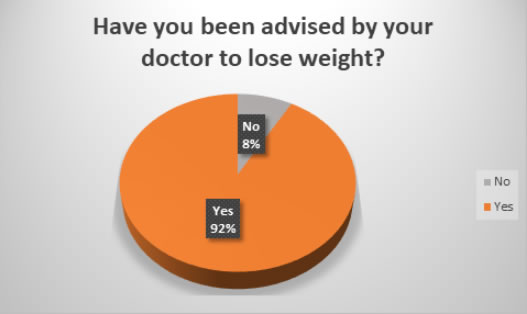
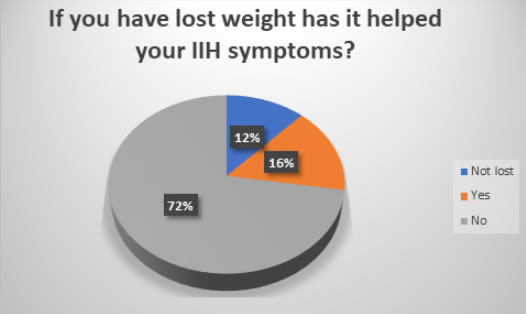
Participants were also asked if they had been advised by their medical professionals to lose weight and if they had had it impacted on their symptoms.
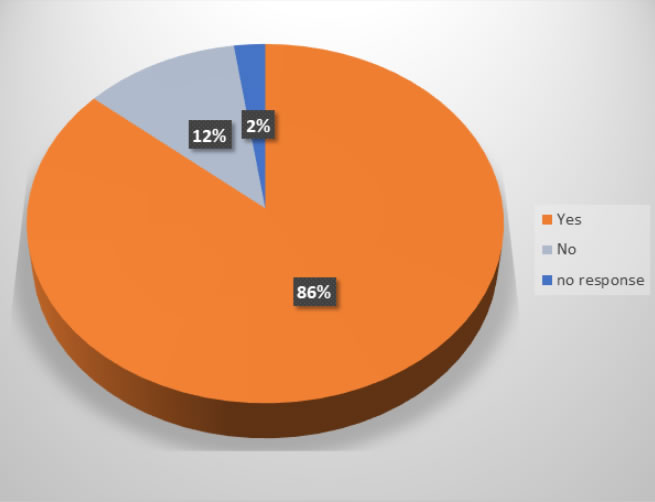
Participants were also asked whether exercise exacerbated their IIH symptoms and if so which symptoms.
When asked to rank the perceived barriers to weight loss and exercise top 3 barriers were identified for each.
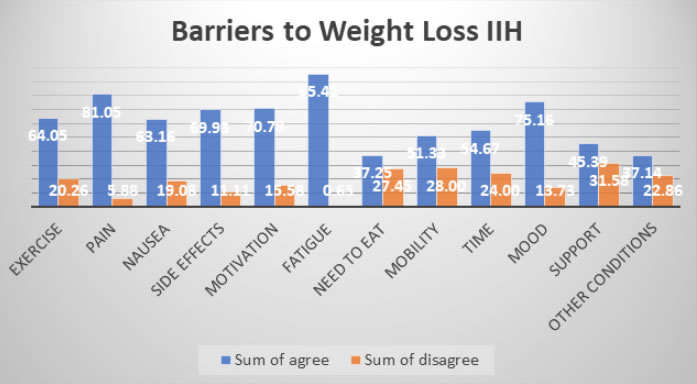
Barriers to weight loss
TOP 3: Fatigue, Pain, Mood
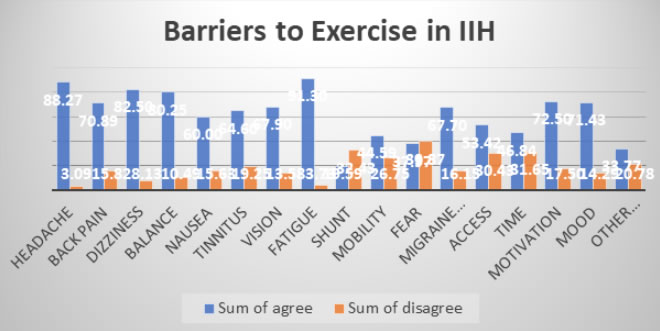
Barriers to exercise
TOP 3: Fatigue, Headache, Dizziness
Conclusion
Top 3 perceived barriers to weight loss – Fatigue, Pain and Mood
Top 3 perceived barriers to exercise – Fatigue, Headache and Dizziness
The results show that further research is needed to understand why some people with IIH experience exacerbations of their IIH symptoms with exercise. Explore what type of exercise is best for pwIIH and that there is a need to explore the barriers to weight loss and exercise with pwIIH at greater depth.







